14 Must-Know Linux Commands to Improve Your Efficiency as a Developer
Background
As a junior developer, I faced a common problem: my laptop was hanging and I needed to free up system resources by terminating unnecessary processes. However, I wasn’t sure how to identify which processes were running and which ones I could safely terminate.
That’s when I started exploring some advanced commands that could help me identify and manage system processes more effectively.
Today, I will be sharing some commands that may be helpful in improving your knowledge and productivity.
Let’s take a step toward the commands.
Sponsored
Want to build good habits but procrastinated? You can try justly.
Introduction
The Linux operating system offers a vast array of powerful tools and commands that can be used to streamline workflows and enhance productivity.
While many developers may be familiar with common commands like ls, cd, and grep, there are many lesser-known commands that can provide valuable functionality for a variety of use cases.
Whether you’re struggling with system performance issues like I was or looking to improve your productivity and efficiency, these commands will help you work more effectively on Linux systems.
1. tree — Learn directory structure
The tree command is a useful utility in Linux that allows you to display the directory structure in a tree-like format. This command can be used to display the contents of a directory and its subdirectories, with all the files and folders listed in an indented manner.
Example
cd into the directory and run the below command,
# Basic Usage
tree
# Display Directory Only
tree -d
# Limit Depth of Tree
tree -L 2Output
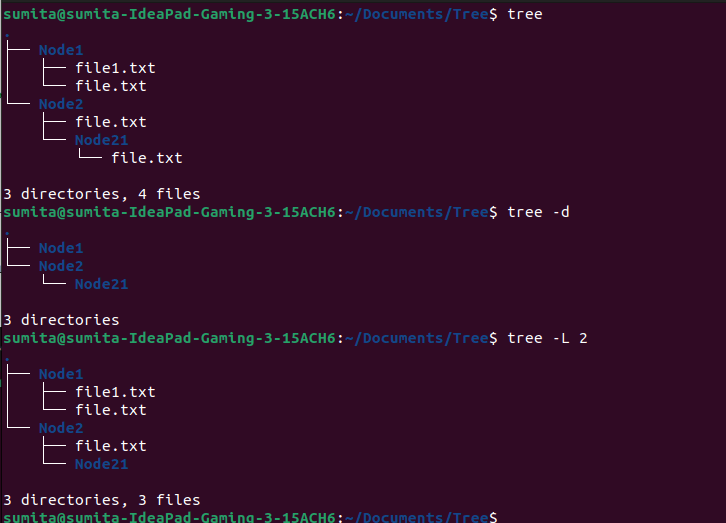
Find more about a tree on Linuxhandbook.
2. ncdu — NCurses Disk Usage
This command is a disk usage analyzer that displays the disk usage of files and directories in a tree-like format.
It is a useful tool for identifying large files or directories that are taking up too much space on your hard drive.
Example
cd into the directory and run the below command,
# Basic Usage
ncdu
# For specific directory
ncdu /dir
# Exclude directory
ncdu -x dirOutput
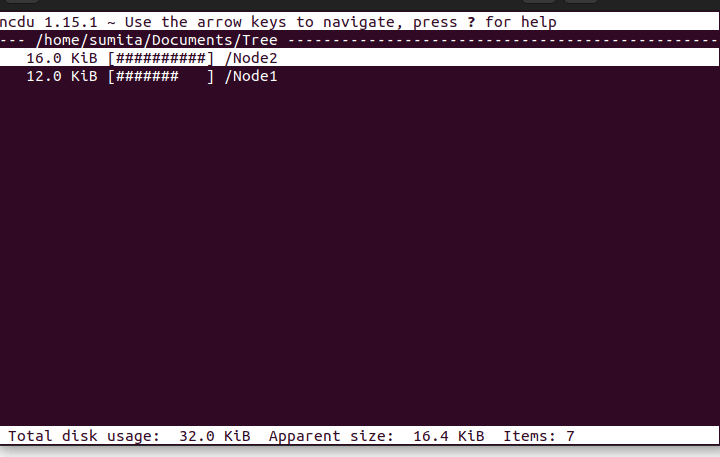
Learn more about ncdu on linuxman.
3. colordiff — The difference between two files
Have you ever checked the difference between two files online? You can see that with command also.
This command is a tool that highlights the differences between two files. It can be used to compare any two text files, and it can be especially useful when comparing code or configuration files.
Example
# Basic Usage
colordiff file1.txt file2.txt
# Ignore Whitespace
colordiff -w file1.txt file2.txt
# Recursive Comparison
# recursively compare two directories and display the differences
# between all the files in the directories
colordiff -r dir1/ dir2/
# Save Output to a File
colordiff file1.txt file2.txt > diff.txtOutput:
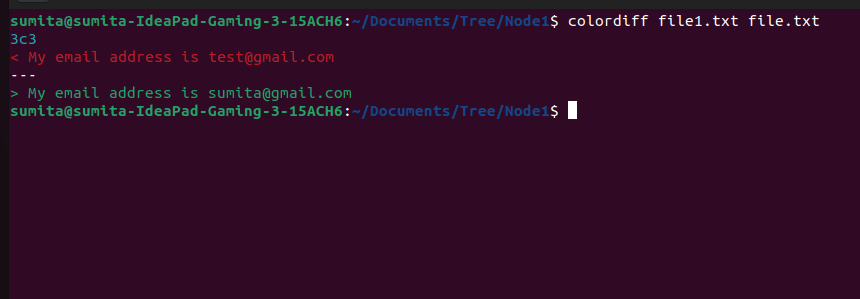
You can find more information from colordiff
4. nohup — Run a script in the background
This Linux command allows you to run a command or script in the background even after you log out or close the terminal. When you run a command with nohup, it becomes immune to hangups and continues to run even if the terminal is closed or disconnected.
Example
# run script.sh in bakcground and save output to the nohup.out
nohup ./script.sh &
# Ssave output to the output.log
nohup ./script.sh -o output.log &
# run a command or script on a remote server
nohup ssh user@server 'command' &
- & symbol is used to start the command in the background
- user is the username for the remote server
- The server is the hostname or IP address of the remote server
- The command is the command or script that you want to run on the remote server.
5. tac — Reverse of cat
This command is a Linux/Unix utility that is used to concatenate and print files in reverse order. It is the opposite of the cat command, which prints the files in the order they appear on the command line.
Example
If you want to reverse the lines of files, you can use tac like below,
tac file.txtOutput
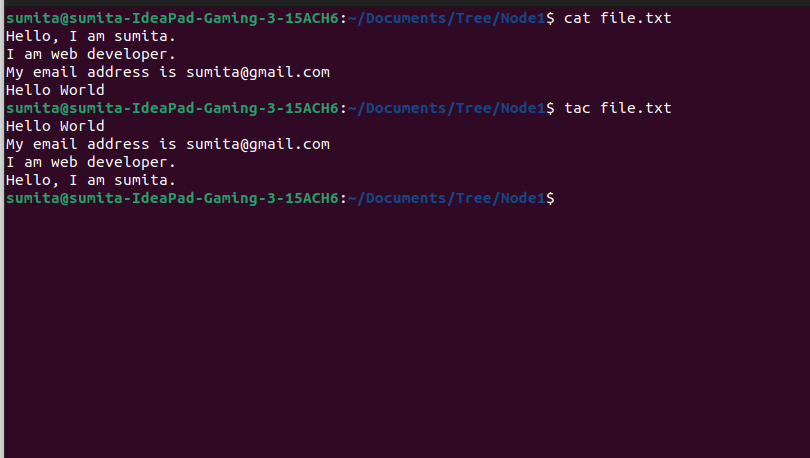
6. units — Unit conversions
This command in Linux is a useful utility for performing unit conversions. It is designed to handle conversions between units of measurement for a wide range of quantities including length, volume, mass, temperature, time, and more.
Example
# simply write units and will prompt some questions
unitsHere is a sample flow,
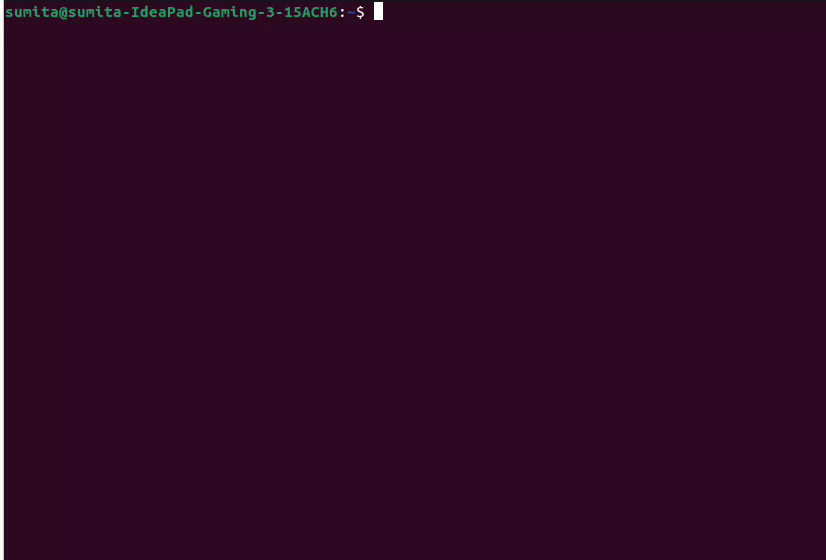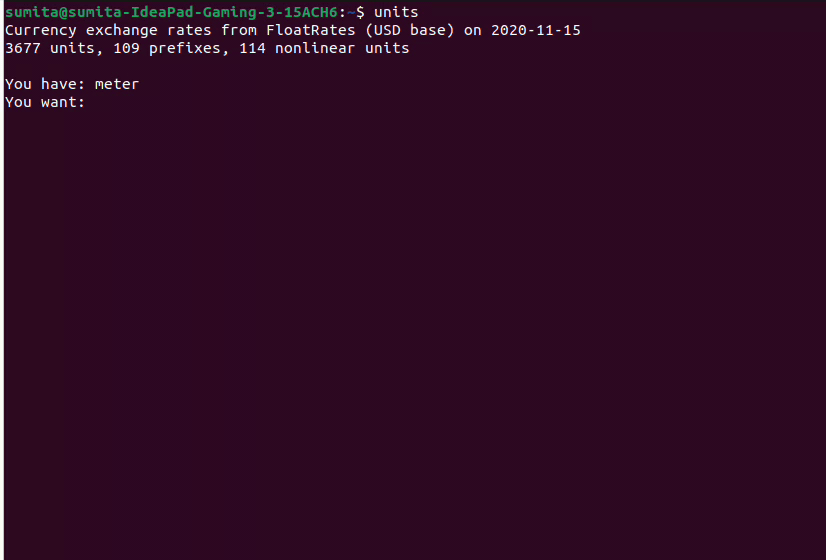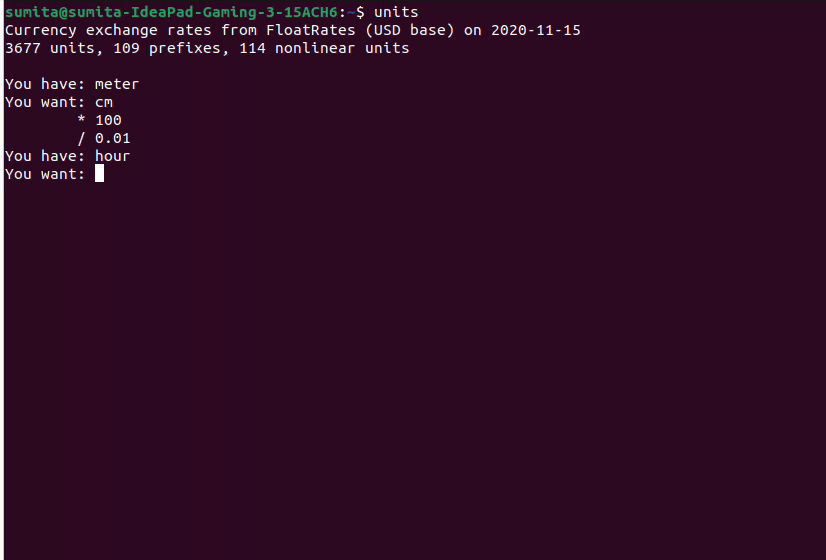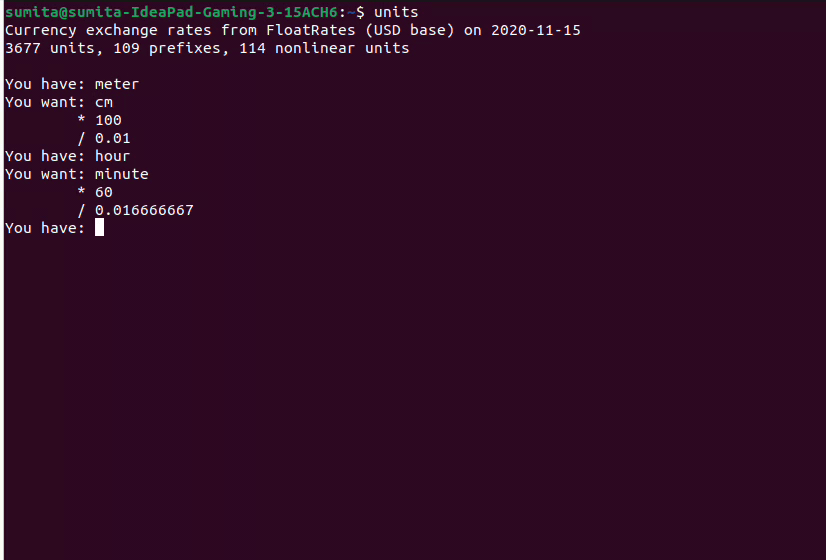
- *: multiply the number of
you havewith a given number to getyou want. - /: multiply the number of
you wantwith a given number to getyou have
meter/cm example:
- Convert 10 meters to cm: 10m * 100 = 1000cm
- Convert 10 cm to meter: 10cm * 0.01 = 0.1m
hour/min example:
- Convert 3 hours to minutes: 3h * 60 = 160m
- Convert 600 minutes to hours: 600m * 0.016666667 = 10h
7. find — Searching files
This command is a powerful and flexible utility for searching for files and directories in a directory hierarchy. It can search based on various criteria like name, type, size, modification time, owner, and permissions.
Example
# Find all the files in the current directory and its subdirectories
find .
# Find all the files with a specific extension
find . -name "*.txt"
# Find all the files modified within the last 24 hours
find . -type f -mtime -1
# Find all the empty directories
find . -type d -empty
# Find all the files smaller than a specific size
find . -type f -size -10MOutput
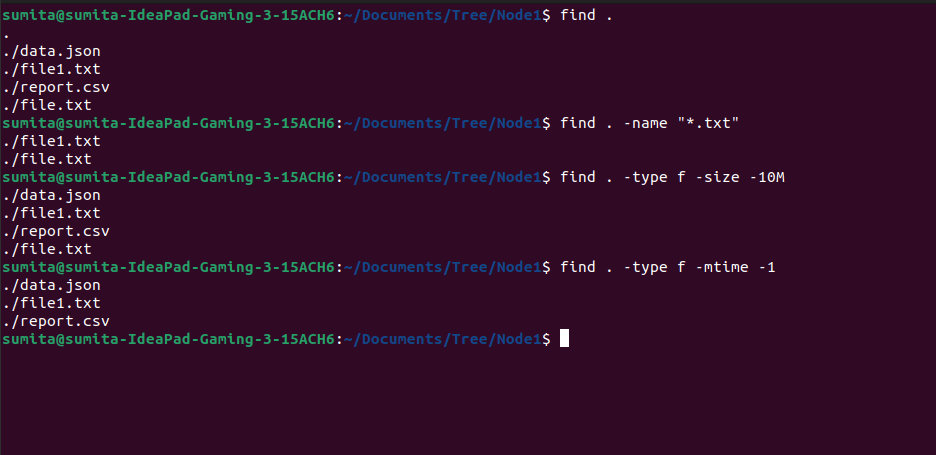
These are a few examples, you can explore more about find with these examples.
8. locate — Quick searching files
This command is used to quickly search for files and directories on a Linux system. Unlike find, which searches the file system for files and directories in real-time, locate uses a pre-built database to quickly find files based on a search term.
Example
# Search for a file by name
locate file.txt
# Search for a file in a specific directory
locate -r /home/user/documents/filename.*
# Limit search results to a specific number
locate -n 10 file.txt
# Update the locate database
# It is a good idea to run this command periodically
# to ensure that the database is up-to-date
sudo updatedbYou can try this and other examples to learn more about this.
9. xxd — Hex dumps of binary files
There are certain situations, such as debugging binary files, reverse engineering, or performing data manipulations, where it is necessary to generate hex dumps of binary files.
This command is a powerful tool for creating hex dumps of binary files and displaying them in a variety of formats.
Example
# create hex dump of file
xxd file.txt
# Displaying the hex dump in a binary format
xxd -b file.txtOutput:
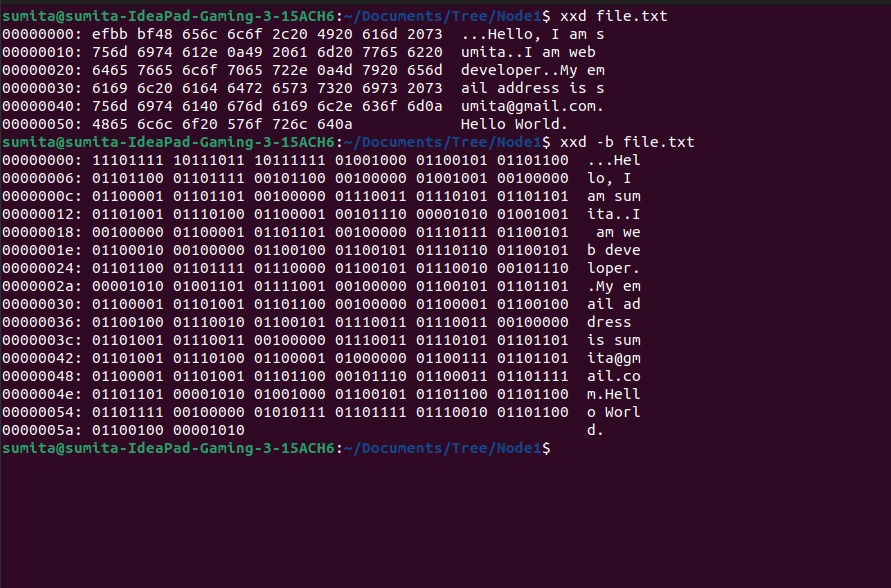
Additional flags are also available like -u(decimal format), -e(little-endian format), and many others.
You can explore more about it on the linuxhandbook.
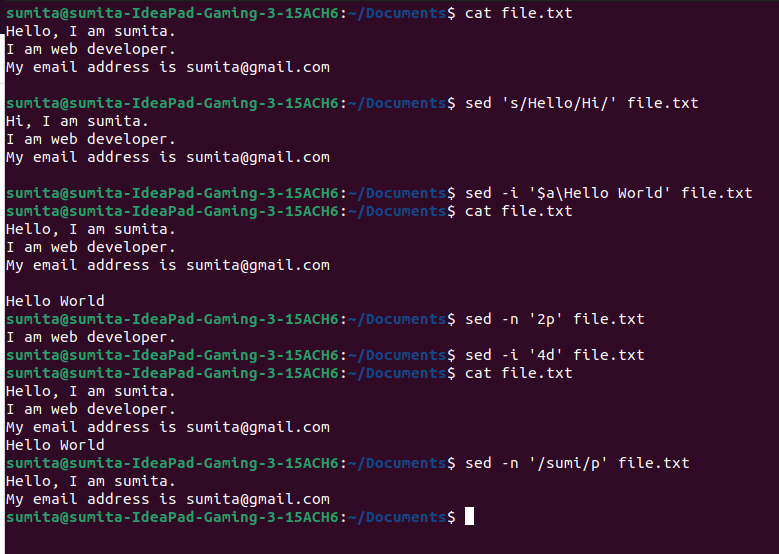
10. sed — Stream Editor
This is a powerful tool for manipulating text in Unix/Linux systems. It is often used to perform search-and-replace operations, as well as to filter and transform text streams. In this section, we will explore the basic usage of the sed command along with some real-time examples.
Example
# search and replace
sed 's/Hello/Hi/' file.txt
# append
sed -i '$a\Hello World' file.txt
# printing
sed -n '2p' file.txt
# deleting
sed -i '3d' file.txt
#Reading from a file
sed -n '/sumi/p' file.txtOutput
11. jq — Parse JSON data
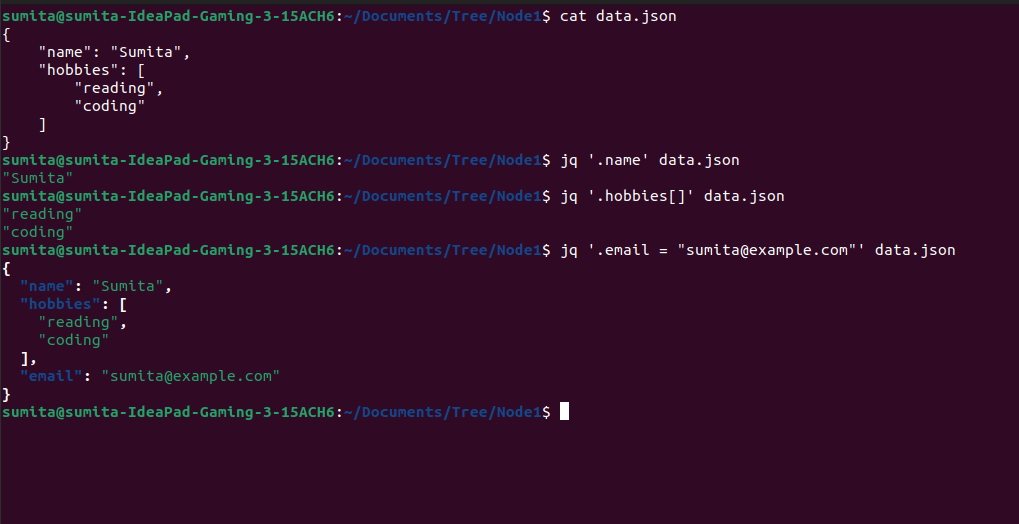
It is a command-line tool for parsing JSON data. It is particularly useful for working with JSON data on the command line, as it allows you to easily filter, transform and manipulate the data.
You can use jq to parse JSON data from a file or from the output of a command. For example, if you have a file data.json containing the following JSON data:
{
"name": "Sumita",
"hobbies": [
"reading",
"coding"
]
}Example
# get name
jq '.name' data.json
# get hobbies
jq '.hobbies[]' data.json
# append email
jq '.email = "sumita@example.com"' data.jsonOutput
Visit linode for an advanced tutorial on jq.
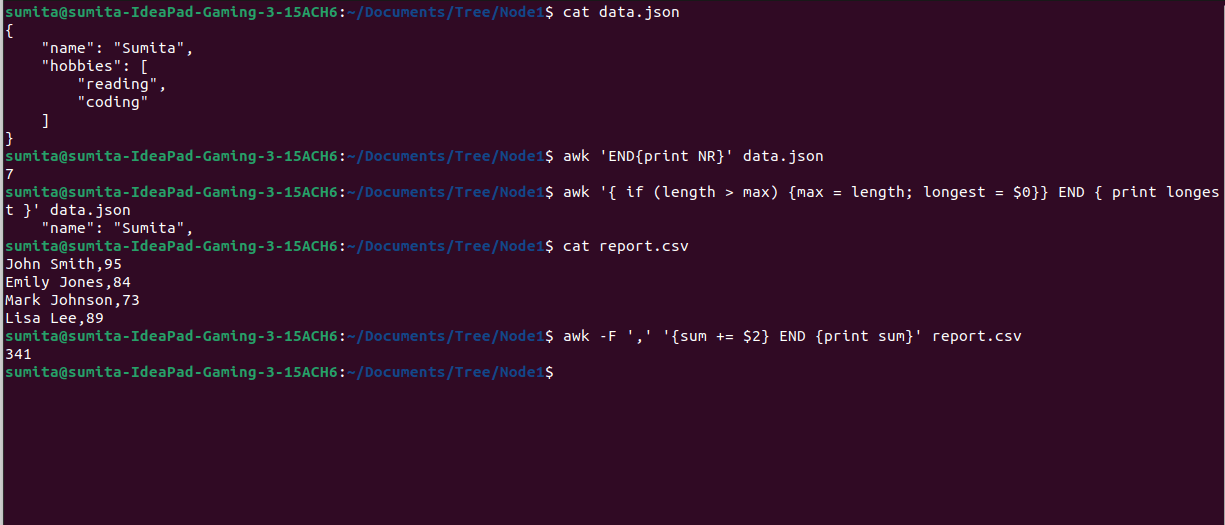
12. awk — Data processing and extractions
It is a powerful command-line tool used for data processing and extraction. It is particularly useful for manipulating structured text files like JSON or CSV and generating reports. awk reads a file line by line and performs operations on each line based on specified patterns and actions.
Example
# Counting number of lines in file
awk 'END{print NR}' filename
# Finding the longest line in a file
awk '{ if (length > max) {max = length; longest = $0}} END { print longest }' filename
# find sum of numbers in file
awk -F ',' '{sum += $2} END {print sum}' filenameOutput:
linuxhandbook has more examples on awk if you want to explore.
13. strace — Diagnose program issues
This command is a powerful debugging tool in Linux that can help you diagnose problems with applications by tracing system calls and signals. It allows you to monitor the interactions between an application and the Linux kernel in real-time.
strace can be used to trace and diagnose problems in any program that runs on Linux, including programs written in JavaScript, Python, PHP, and any other language.
Example
Suppose you have a program called myprog that is crashing or behaving unexpectedly. You can use strace to trace its system calls and find out issues using the below command,
strace -o myprog.log myprogThis will start the myprog command and all the output will be written to the file myprog.log.
Next, reproduce the issue or run the program for a few seconds and then stop it by pressing CTRL-C.
Once you have stopped the program, you can use various tools like grep to analyze the strace output in the myprog.log file and find the root problems.
You can explore more about strace on linuxman.
14. scp — Secure copy
This command is a command-line tool that allows you to securely transfer files between a local and a remote system over an SSH (Secure Shell) connection. It uses the same authentication and security mechanisms as SSH to protect your data while in transit.
Example
# copy file.txt to remote server at /home/user location
scp file.txt user@remote:/home/user/
# copy file.txt from remote server to local server's current location
scp user@remote:/home/user/file.txt .Conclusion
These commands can greatly enhance the productivity of developers and system administrators, making their work more efficient and effective. With a deeper understanding of these commands, they can optimize their workflows and streamline their tasks.
We’re Grateful to have you with us on this journey!
Suggestions and feedback are more than welcome!
Please reach us at Canopas Twitter handle @canopassoftware with your content or feedback. Your input enriches our content and fuels our motivation to create more valuable and informative articles for you.
Related Article

