Live Streaming and Audio Equalizer with ExoPlayer in Jetpack Compose
Background
ExoPlayer, coupled with the capabilities of Media3, offers a robust solution for playing multimedia content in Android applications. In this tutorial, we’ll go through setting up ExoPlayer with Media3 to support live streaming using M3U8 URLs. Additionally, we’ll explore how to integrate an audio equalizer to provide users with a personalized audio experience.
Live streaming with ExoPlayer involves the real-time playback of multimedia content over the internet using the powerful capabilities of the ExoPlayer library.
In this exploration, we’ll delve into the intricacies of how ExoPlayer facilitates the seamless playback of live-stream URLs, offering an immersive experience for users.
What we’ll implement in this blog?
The source code is available on GitHub.
Sponsored
Empower your journey to well-being with Justly. Your life is your greatest wealth — let us be your guide on the path to a happier you!
How Live Streaming Works with ExoPlayer?
Live streaming using ExoPlayer revolves around efficiently handling the transmission of audio and video content in real-time. The process encompasses several key stages:
- Content Source: The live content, whether it’s a sports event, a concert, or a news broadcast, is captured using cameras and microphones. This live feed is then made available for streaming.
- Encoding: The captured content is encoded into a digital format suitable for streaming. This involves compressing and converting the raw audio and video data into a format compatible with streaming protocols.
- Streaming Server: The encoded data is sent to a streaming server, acting as a central hub. This server manages the live content distribution to multiple viewers by sending data packets to their devices.
- ExoPlayer Integration: ExoPlayer, with its robust capabilities, is integrated into the application to handle the playback of the live stream. The application fetches the live stream URL and configures ExoPlayer to handle the streaming protocol (such as HLS or DASH).
- Viewer’s Device: Users access the live stream through various devices, including smartphones, tablets, computers, or smart TVs. The ExoPlayer instance on the viewer’s device decodes the received data, enabling them to watch or listen to the live content in real-time.
Setting Up ExoPlayer for Live Streaming
To integrate ExoPlayer into our application for live streaming, we need to follow these key steps:
Add Dependencies
Include the necessary dependencies in the project’s build.gradle file:
// Exoplayer dependencies
implementation("androidx.media3:media3-exoplayer:1.2.0")
implementation("androidx.media3:media3-ui:1.2.0")
implementation("androidx.media3:media3-exoplayer-hls:1.2.0")These dependencies ensure that the application can leverage the features of ExoPlayer for live streaming.
Create ExoPlayerManager
We’ll create a manager class to handle ExoPlayer instances. This ensures a single-player instance throughout the app’s lifecycle.
object ExoPlayerManager {
private var exoPlayer: ExoPlayer? = null
fun getExoPlayer(context: Context): ExoPlayer {
if (exoPlayer == null) {
exoPlayer = ExoPlayer.Builder(context).build()
}
return exoPlayer!!
}
fun releaseExoPlayer() {
exoPlayer?.release()
exoPlayer = null
}
}Initialize ExoPlayer
Within your Composable function, initialize ExoPlayer with a sample HLS stream URL:
@Composable
fun LiveStreamingScreen() {
// Obtain the current context and lifecycle owner using LocalContext and LocalLifecycleOwner
val context = LocalContext.current
val lifecycleOwner = LocalLifecycleOwner.current
// Remember the ExoPlayer instance to persist across recompositions
val exoPlayer = remember { ExoPlayerManager.getExoPlayer(context) }
// Launch an effect to initialize ExoPlayer and set up the media source
LaunchedEffect(key1 = Unit) {
// Create a data source factory for handling media requests
val dataSourceFactory = DefaultHttpDataSource.Factory()
// Define the URI for the sample HLS stream
val uri = Uri.Builder()
.encodedPath("http://sample.vodobox.net/skate_phantom_flex_4k/skate_phantom_flex_4k.m3u8")
.build()
val mediaItem = MediaItem.Builder().setUri(uri).build()
// Create an HlsMediaSource from the media item for handling HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) content
val internetVideoSource =
HlsMediaSource.Factory(dataSourceFactory).createMediaSource(mediaItem)
exoPlayer.setMediaSource(internetVideoSource)
exoPlayer.prepare()
// Will be used in later implementation for Equalizer
viewModel.onStart(exoPlayer.audioSessionId)
}
// ...
}Display ExoPlayer View
Integrate the ExoPlayer view into your Composable function
// ...
Box(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) {
AndroidView(
modifier =
Modifier.fillMaxWidth()
.aspectRatio(1.4f)
.padding(top = 16.dp)
.background(Color.Black),
factory = {
PlayerView(context).apply {
// Connect the ExoPlayer instance to the PlayerView
player = exoPlayer
// Configure ExoPlayer settings
exoPlayer.repeatMode = Player.REPEAT_MODE_ONE
exoPlayer.playWhenReady = false
useController = true
}
}
)
}
// ...Observe Lifecycle Events and Release Resources
Set up DisposableEffects to observe lifecycle events and release the ExoPlayer when the composable is disposed:
// ...
// Observe lifecycle events (e.g., app resume and pause)
// and adjust ExoPlayer's playback state accordingly.
DisposableEffect(key1 = lifecycleOwner) {
val observer = LifecycleEventObserver { _, event ->
if (event == Lifecycle.Event.ON_RESUME) {
exoPlayer.playWhenReady = true
} else if (event == Lifecycle.Event.ON_PAUSE) {
exoPlayer.playWhenReady = false
}
}
lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.addObserver(observer)
onDispose {
lifecycleOwner.lifecycle.removeObserver(observer)
}
}
// Release the ExoPlayer when the composable is disposed
// This helps in proper resource management
DisposableEffect(key1 = Unit) {
onDispose { ExoPlayerManager.releaseExoPlayer() }
}
// ...With the above code, we have successfully set up ExoPlayer for live streaming! You can check out the final code from here.
Setting Up Audio Equalizer
Now, let’s explore how to integrate an audio equalizer into an Exoplayer setup using Jetpack Compose. This will allow users to customize the audio experience by adjusting preset equalizer settings or creating a custom equalizer configuration.
An audio equalizer enhances the user experience by providing fine-grained control over the audio output.
Add Dependencies
Include the necessary dependencies in your project’s build.gradle file:
//hilt
implementation("com.google.dagger:hilt-android:2.48")
kapt("com.google.dagger:hilt-android-compiler:2.47")
implementation("androidx.hilt:hilt-navigation-compose:1.1.0")
//Gson
implementation("com.google.code.gson:gson:2.9.1")These dependencies ensure that your application can leverage the features of the Hilt for dependency injection and Gson for efficiently storing complex data in preferences.
Define Equalizer Presets and Gain Values
We define a set of presets, such as “Flat,” “Acoustic,” and “Rock,” each with corresponding gain values that control the audio frequencies. These presets will serve as starting points for users to customize their audio experience.
// Equalizer presets and gain values
val effectType = arrayListOf(
"Custom", "Flat", "Acoustic", "Dance",
"Hip Hop", "Jazz", "Pop", "Rock", "Podcast"
)
// Constants for presets
const val PRESET_CUSTOM = 0
const val PRESET_FLAT = 1
const val PRESET_ACOUSTIC = 2
const val PRESET_DANCE_LOUNGE = 3
const val PRESET_HIP_HOP = 4
const val PRESET_JAZZ_BLUES = 5
const val PRESET_POP = 6
const val PRESET_ROCK = 7
const val PRESET_PODCAST = 8
// Gain values for each preset
val FLAT = arrayListOf(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
val ACOUSTIC = arrayListOf(0.44, 0.12, 0.12, 0.34, 0.2)
val DANCE = arrayListOf(0.52, 0.08, 0.28, 0.48, 0.06)
val HIP_HOPE = arrayListOf(0.44, 0.06, -0.14, 0.1, 0.38)
val JAZZ = arrayListOf(0.32, 0.0, 0.22, 0.1, 0.2)
val POP = arrayListOf(-0.14, 0.28, 0.38, 0.22, -0.2)
val ROCK = arrayListOf(0.38, 0.2, -0.04, 0.02, 0.34)
val PODCAST = arrayListOf(-0.12, 0.26, 0.36, 0.16, -0.2)Create Audio Effect Data Class
The AudioEffects data class holds crucial information about the selected effect type and the corresponding gain values. This data class acts as a bridge between user preferences and the actual implementation of the audio equalizer.
// Data class representing audio effects configuration
data class AudioEffects(
var selectedEffectType: Int = 0,
var gainValues: ArrayList<Double>
)Here, selectedEffectType represents the chosen audio preset, and gainValues store the customized gain values for different frequency bands. This data class encapsulates the user's audio preferences.
Create AppModule for Dependency Injection
For clean and modular dependency injection, we introduce the AppModule. This module, annotated with @InstallIn(SingletonComponent::class), provides essential dependencies such as Gson and SharedPreferences.
@Module
@InstallIn(SingletonComponent::class)
class AppModule {
@Provides
@Singleton
fun provideGson(): Gson {
val gsonBuilder = GsonBuilder()
return gsonBuilder.create()
}
@Named(AUDIO_EFFECT_PREFERENCES)
@Provides
fun provideAudioEffectPreferences(application: Application): SharedPreferences {
return application.getSharedPreferences(AUDIO_EFFECT_PREFERENCES, Context.MODE_PRIVATE)
}
}In this module, provideGson offers a singleton instance of Gson, while provideAudioEffectPreferences provides a named SharedPreferences instance specifically for audio effect preferences. This module will be crucial for managing dependencies throughout the application.
Implement Equalizer Preferences with SharedPreferences and Gson
To provide a seamless user experience, we’ll utilize SharedPreferences to persist user preferences related to the audio equalizer. Additionally, we use GSON for efficient data serialization, allowing us to convert complex data structures into a format that can be easily stored and retrieved. By creating an EqualizerPreferences class, we ensure that users don't have to set their equalizer preferences repeatedly.
const val AUDIO_EFFECT_PREFERENCES = "audio_effect_preferences"
private const val AUDIO_EFFECT_IS_EQUALIZER_ENABLED = "is_equalizer_enabled"
private const val AUDIO_EFFECT_EQUALIZER_SETTING = "equalizer_audio_effect"
private const val AUDIO_EFFECT_LOWEST_BAND_LEVEL = "equalizer_lowest_band_level"
@Singleton
class EqualizerPreferences
@Inject constructor(
@param:Named(AUDIO_EFFECT_PREFERENCES) private val sharedPreferences: SharedPreferences,
private val gson: Gson
) {
var isEqualizerEnabled: Boolean
get() = sharedPreferences.getBoolean(AUDIO_EFFECT_IS_EQUALIZER_ENABLED, false)
set(isEnable) = sharedPreferences.edit()
.putBoolean(AUDIO_EFFECT_IS_EQUALIZER_ENABLED, isEnable).apply()
// Getting and setting the user's audio preferences
var audioEffects: AudioEffects?
get() {
val json = sharedPreferences.getString(AUDIO_EFFECT_EQUALIZER_SETTING, null)
if (json != null) {
try {
return gson.fromJson(json, AudioEffects::class.java)
} catch (t: Throwable) {
t.printStackTrace()
}
}
return null
}
set(audioEffects) {
var json: String? = null
if (audioEffects != null) {
json = gson.toJson(audioEffects)
}
sharedPreferences.edit().putString(AUDIO_EFFECT_EQUALIZER_SETTING, json).apply()
}
var lowestBandLevel: Int
get() = sharedPreferences.getInt(AUDIO_EFFECT_LOWEST_BAND_LEVEL, 0)
set(value) = sharedPreferences.edit().putInt(AUDIO_EFFECT_LOWEST_BAND_LEVEL, value).apply()
}Here, GSON plays a crucial role in converting our AudioEffects data class to a JSON string for storage in SharedPreferences. This ensures a seamless and efficient way to store and retrieve complex data structures.
Create an Audio Equalizer ViewModel
Build a robust AudioEqualizerViewModel responsible for managing the audio equalizer logic. This ViewModel initializes the equalizer, handles preset selections, and updates settings based on user interactions.
@HiltViewModel
class AudioEqualizerViewModel @Inject constructor(
private val equalizerPreferences: EqualizerPreferences
) : ViewModel() {
// MutableStateFlow to observe and emit changes in audio effects
val audioEffects = MutableStateFlow<AudioEffects?>(null)
// Instance of the Equalizer class from the Android system library
private var equalizer: Equalizer? = null
// MutableStateFlow to observe and emit changes in the equalizer's enable/disable state
val enableEqualizer = MutableStateFlow(false)
// Unique audio session ID associated with the Exoplayer
private var audioSessionId = 0
init {
// Retrieve and set the initial equalizer enable/disable state and audio effects from preferences
enableEqualizer.value = equalizerPreferences.isEqualizerEnabled
audioEffects.tryEmit(equalizerPreferences.audioEffects)
if (audioEffects.value == null) {
audioEffects.tryEmit(AudioEffects(PRESET_FLAT, FLAT))
}
}
// Will be called when exoplayer instance is created and we have audioSessionId
fun onStart(sessionId: Int) {
audioSessionId = sessionId
equalizer?.enabled = enableEqualizer.value
equalizer = Equalizer(Int.MAX_VALUE, audioSessionId)
// Set the lowest band level based on the equalizer's capabilities
equalizerPreferences.lowestBandLevel = equalizer?.bandLevelRange?.get(0)?.toInt() ?: 0
// Apply gain values to the equalizer based on the stored audio effects
audioEffects.value?.gainValues?.forEachIndexed { index, value ->
val bandLevel = (value * 1000).toInt().toShort()
equalizer?.setBandLevel(index.toShort(), bandLevel)
}
}
// Method called when a preset is selected
fun onSelectPreset(presetPosition: Int) {
// Return if no audio effects are available
if (audioEffects.value == null) return
// Determine the gain values based on the selected preset
val gain = if (presetPosition == PRESET_CUSTOM) {
ArrayList(audioEffects.value!!.gainValues)
} else {
ArrayList(getPresetGainValue(presetPosition))
}
// Update the audio effects with the selected preset and gain values
audioEffects.tryEmit(AudioEffects(presetPosition, gain))
equalizerPreferences.audioEffects = audioEffects.value
// Apply the gain values to the equalizer
equalizer?.apply {
gain.forEachIndexed { index, value ->
val bandLevel = (value * 1000).toInt().toShort()
setBandLevel(index.toShort(), bandLevel)
}
}
}
// Method called when a specific band level is changed by the user
fun onBandLevelChanged(changedBand: Int, newGainValue: Int) {
// Retrieve the lowest band level from preferences
val lowest = equalizerPreferences.lowestBandLevel
// Calculate the new band level
val bandLevel = newGainValue.plus(lowest)
// Apply the new band level to the equalizer
equalizer?.setBandLevel(changedBand.toShort(), bandLevel.toShort())
val list = ArrayList(audioEffects.value!!.gainValues)
list[changedBand] = (newGainValue.toDouble() / 1000)
audioEffects.tryEmit(
AudioEffects(
PRESET_CUSTOM,
list
)
)
equalizerPreferences.audioEffects = audioEffects.value
}
// Method called to toggle the equalizer's enable/disable state
fun toggleEqualizer() {
enableEqualizer.tryEmit(!enableEqualizer.value)
equalizer?.enabled = enableEqualizer.value
equalizerPreferences.isEqualizerEnabled = enableEqualizer.value
if (!enableEqualizer.value) {
audioEffects.tryEmit(AudioEffects(PRESET_FLAT, FLAT))
equalizerPreferences.audioEffects = audioEffects.value
}
}
// Method to retrieve gain values for a specific preset
private fun getPresetGainValue(index: Int): List<Double> {
return when (index) {
PRESET_FLAT -> FLAT
PRESET_ACOUSTIC -> ACOUSTIC
PRESET_DANCE_LOUNGE -> DANCE
PRESET_HIP_HOP -> HIP_HOPE
PRESET_JAZZ_BLUES -> JAZZ
PRESET_POP -> POP
PRESET_ROCK -> ROCK
PRESET_PODCAST -> PODCAST
else -> FLAT
}
}
}This ViewModel efficiently manages the audio equalizer’s state, handles user interactions, and ensures that user preferences are persisted using SharedPreferences.
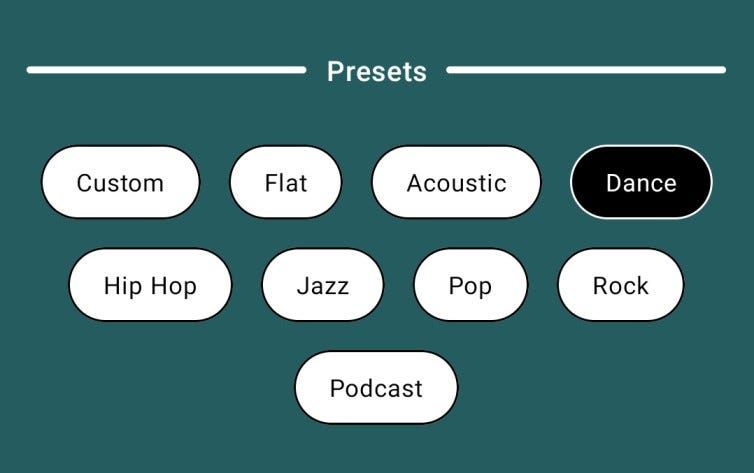
Develop Equalizer SwitchView, PresetsView & EqualizerView Composable
Design a user-friendly Equalizer Switch, EqualizerViewandPresetsView composable to allow users to visualize and adjust equalizer settings. The switch will allow users to enable/disable the audio settings using Equalizer and EqualizerView will include sliders for different frequency bands, providing a highly customizable audio experience. PresetsView will contain some pre-defined effect types to apply directly to the equalizer.
Switch View
Row(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceBetween,
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.equalizer_title_text),
fontSize = MaterialTheme.typography.titleLarge.fontSize,
fontWeight = FontWeight.SemiBold,
color = Color.White
)
Switch(
checked = enableEqualizer,
onCheckedChange = {
// Toggle the equalizer's enable/disable state
viewModel.toggleEqualizer()
},
colors =
SwitchDefaults.colors(
checkedTrackColor = Color.Black,
checkedIconColor = Color.Black,
uncheckedTrackColor = Color.White,
uncheckedBorderColor = Color.Black,
)
)
}
EqualizerView
@OptIn(ExperimentalMaterial3Api::class)
@Composable
fun EqualizerView(viewModel: AudioEqualizerViewModel) {
// Frequency labels for the equalizer bands
val xAxisLabels = listOf("60Hz", "230Hz", "910Hz", "3kHz", "14kHz")
// Collect the current state of audio effects from the ViewModel
val audioEffects by viewModel.audioEffects.collectAsState()
// Column layout to arrange UI elements vertically
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.fillMaxHeight()
.graphicsLayer {
// Rotate the entire column to display frequency labels/sliders vertically
rotationZ = 270f
},
verticalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceEvenly,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
// Iterate through frequency labels and create corresponding UI elements
for (index in xAxisLabels.indices) {
Row(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(top = 20.dp)
.width(220.dp)
) {
// Each frequency label and its corresponding slider are placed in a Box
Box {
// Display the frequency label with rotation
Text(
text = xAxisLabels[index],
modifier = Modifier
.wrapContentWidth()
.align(Alignment.CenterStart)
.rotate(90f),
color = Color.White,
fontSize = 8.sp,
textAlign = TextAlign.Start
)
// Slider component for adjusting the gain value of each frequency band
Slider(
modifier = Modifier
.offset(x = 20.dp),
// Bind the slider value to the corresponding gain value from the ViewModel
value = audioEffects!!.gainValues[index].times(1000f).toFloat()
.coerceIn(-3000f, 3000f),
onValueChange = {
// Notify the ViewModel when a slider value changes
viewModel.onBandLevelChanged(index, it.toInt())
},
valueRange = -3000f..3000f,
colors = SliderDefaults.colors(
thumbColor = Color.Black,
activeTrackColor = Color.Black,
inactiveTrackColor = Color.White
),
thumb = {
// Customized appearance of the slider's thumb
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(20.dp)
.border(
1.dp,
Color.White,
CircleShape
)
.clip(CircleShape)
.background(Color.Black, CircleShape)
)
}
)
}
}
}
}
}PresetsView
@Composable
fun PresetsView(viewModel: AudioEqualizerViewModel) {
// Collect the current state of audio effects from the ViewModel
val audioEffects by viewModel.audioEffects.collectAsState()
// Group the effect types into chunks of 4 for layout
val groupedList = effectType.chunked(4)
// Row containing the title and dividers
Row(
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically
) {
Divider(
modifier = Modifier
.weight(1f)
.height(4.dp)
.clip(RoundedCornerShape(4.dp)),
color = Color.White,
thickness = 1.dp
)
// Title text
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.presets_title_text),
fontSize = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium.fontSize,
fontWeight = FontWeight.Medium,
color = Color.White,
modifier = Modifier
.wrapContentWidth()
.weight(0.5f)
.padding(4.dp)
.zIndex(1f),
textAlign = TextAlign.Center
)
Divider(
modifier = Modifier
.weight(1f)
.height(4.dp)
.clip(RoundedCornerShape(4.dp)),
color = Color.White,
thickness = 1.dp
)
}
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(20.dp))
// Iterate through grouped effect types and create UI elements
for (itemList in groupedList) {
BoxWithConstraints(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
) {
// Calculate padding and spacing based on screen width
val horizontalPadding =
if (maxWidth < 320.dp) 8.dp else if (maxWidth > 400.dp) 40.dp else 20.dp
val horizontalSpacing = if (maxWidth > 400.dp) 24.dp else 16.dp
// Row containing individual preset items
Row(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(vertical = 8.dp),
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(
space = horizontalSpacing,
alignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
),
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically
) {
for (item in itemList) {
// Get the index of the current item
val index by remember {
mutableIntStateOf(
effectType.indexOf(
item
)
)
}
// Create a clickable preset item
BoxWithConstraints(
modifier = Modifier
.wrapContentSize()
.border(
1.dp,
if (index == audioEffects?.selectedEffectType) Color.White else Color.Black,
RoundedCornerShape(40.dp)
)
.clip(RoundedCornerShape(40.dp))
.clickable {
// Notify the ViewModel when a preset is selected
viewModel.onSelectPreset(index)
}
.background(if (index == audioEffects?.selectedEffectType) Color.Black else Color.White),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
// Display the preset item text
Text(
text = item,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodySmall,
modifier = Modifier
.padding(
horizontal = horizontalPadding,
vertical = 12.dp
),
fontSize = 14.sp,
color = if (index == audioEffects?.selectedEffectType) Color.White else Color.Black,
maxLines = 1,
overflow = TextOverflow.Ellipsis
)
}
}
}
}
}
}
Now, let’s call the above functions from the parent composable with AnimatedVisibility!
@Composable
fun AudioEqualizerScreen() {
val viewModel = hiltViewModel<AudioEqualizerViewModel>()
val enableEqualizer by viewModel.enableEqualizer.collectAsState()
Column {
Row(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxWidth(),
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceBetween,
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically
) {
Text(
text = stringResource(R.string.equalizer_title_text),
fontSize = MaterialTheme.typography.titleLarge.fontSize,
fontWeight = FontWeight.SemiBold,
color = Color.White
)
Switch(
checked = enableEqualizer,
onCheckedChange = { viewModel.toggleEqualizer() },
colors =
SwitchDefaults.colors(
checkedTrackColor = Color.Black,
checkedIconColor = Color.Black,
uncheckedTrackColor = Color.White,
uncheckedBorderColor = Color.Black,
)
)
}
AnimatedVisibility(
visible = enableEqualizer,
enter = fadeIn() + slideInVertically { fullHeight -> -fullHeight / 2 },
exit = fadeOut() + slideOutVertically { fullHeight -> -fullHeight / 3 }
) {
EqualizerView(viewModel = viewModel)
}
AnimatedVisibility(
visible = enableEqualizer,
enter = fadeIn() + slideInVertically { fullHeight -> -fullHeight / 2 },
exit = fadeOut() + slideOutVertically { fullHeight -> -fullHeight / 2 }
) {
PresetsView(viewModel)
}
}
}The source code is available on GitHub.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we’ve laid the foundation for setting up ExoPlayer for live streaming and integrating an audio equalizer in a Jetpack Compose application. This combination provides a seamless user experience for streaming audio with customizable equalizer settings.
Feel free to expand on this codebase to add more features and enhance the overall user experience of your multimedia application.
Happy coding!
Related Article
Whether you need...
- *High-performing mobile apps
- *Bulletproof cloud solutions
- *Custom solutions for your business.
